Wealth Management
Quantum computing: advancing finance and technology

Wealth Management

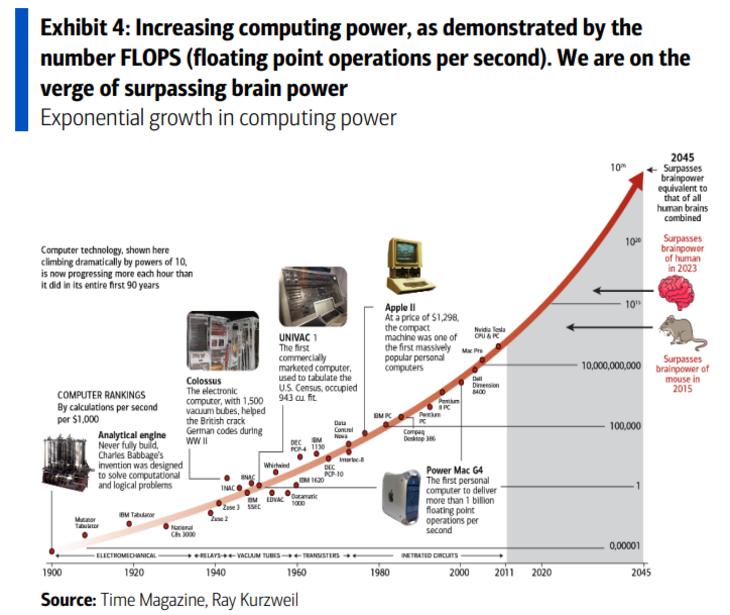
In recent years, quantum computing has rapidly progressed from a theoretical concept to a transformative force in technology and finance, with major companies and governments investing heavily in its development.
Unlike traditional computers, which use classical bits that can be either 0 or 1, quantum computers use qubits that can be both 0 and 1 at the same time thanks to special phenomena called superposition and entanglement. This allows these machines to process a lot of information simultaneously.
Over the last few years, the number of qubits in quantum computers has approximately doubled every 1 to 2 years. Because of this, these computers are becoming much faster at solving certain difficult problems, such as simulating molecules, optimising portfolio, or organising supply-chain.
Since the components of traditional computers are approaching a physical limit and cannot be reduced indefinitely, special algorithms like Shors and Grover’s enable quantum computers to achieve much higher performance.
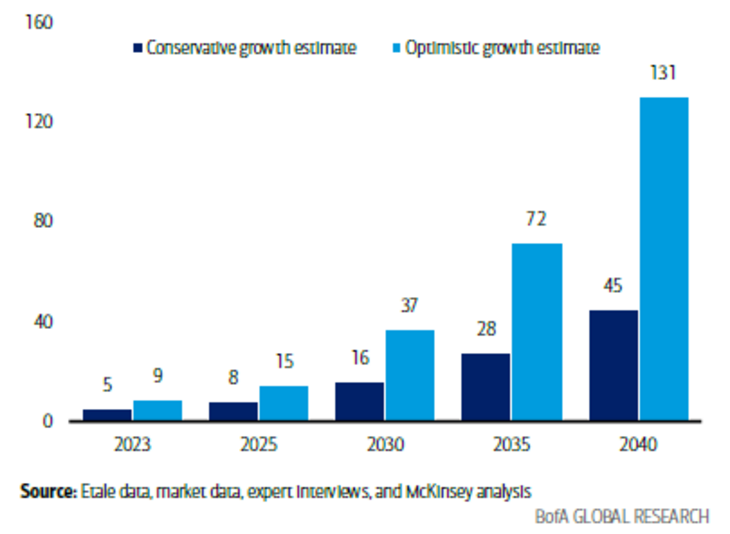
The rapid growth of artificial intelligence is fueling a surge in investment toward quantum computing. Both technologies share the promise of revolutionising how we process and analyse vast amounts of data.
As AI models become more complex, the need for faster and more powerful computational resources grows. Quantum computing offers a pathway to meet these demands, making their convergence a focal point for future innovation.
This synergy could lead to breakthroughs in fields such as drug discovery, climate modeling, and financial forecasting. As research advances, industries are closely watching the intersection of AI and quantum for transformative possibilities.
The potential applications of quantum computing are vast and span a wide range of industries:
Finance
Leading banks such as JPMorgan Chase, Goldman Sachs, and BBVA are testing quantum-powered portfolio optimisation and risk management engines to enhance their decision-making capabilities.
Pharma
Companies like Roche and Boehringer are leveraging quantum simulations to accelerate the identification and prioritisation of promising drug leads.
Energy
Quantum computing is being applied to model fusion plasma behaviour, optimise grid load balancing, and innovate next-generation battery chemistry.
Manufacturing & Logistics
Quantum algorithms help improve predictive maintenance, optimise multi-site routing, and eliminate inventory inefficiencies.
Cybersecurity
Quantum presents a dual narrative: while it threatens to break current cryptographic systems, it also drives the development of quantum-safe security protocols.
Defense & Space
Applications include advanced navigation systems, secure communications, and strategic simulations for defence planning.
Despite its promise, quantum computing faces significant challenges:
Quantum computing has left the laboratories and is now part of tangible business projects. Although it requires significant investment and the outcomes are not always easy to predict, being among the first to adopt it could make all the difference.
Those who start testing this technology now, prepare for quantum security, and monitor its development will have a major advantage. They will be better equipped to capitalise on the opportunities offered by this new technology or to protect themselves against the changes it will bring.
This publication is prepared by Mirabaud. It is not intended to be distributed, disseminated, published or used in any jurisdiction where such distribution, dissemination, publication or use would be prohibited. It is not intended for people or entities to whom it would be illegal to send such publication.
Read more
Continue to
